Proceedings
 home home
 preface preface
 contents contents
 authors authors
 keywords keywords
 copyright copyright
 reference reference
 ©2012 Civil-Comp Ltd
©2012 Civil-Comp Ltd |
 |
 |
 |
P. Moreno-García1, H. Lopes2, J.V. Araújo dos Santos3 and N.M.M. Maia3
1INEGI, Instituto de Engenharia Mecânica e Gestão Industrial, Porto, Portugal
2ESTIG, Instituto Politécnico de Bragança, Portugal
3IDMEC/IST, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: damage localisation, finite element method, Ritz method, higher order spatial derivative, laminated plate.
full paper (pdf) -
reference
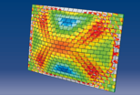
A new vibration based methodology for damage localisation in composite laminated plates is proposed in this paper. The method relies on damage indicators defined as differences of third and fourth order spatial derivatives of modal displacement fields of damaged and undamaged plates. The damage is simulated by prescribing a decrease in the laminate stiffness of an area of the plate, which is discretised in finite elements. Thus, discrete displacement fields are obtained which are differentiated using higher order finite differences. The modal displacement fields of the undamaged plate are obtained using the Ritz method. Therefore, a direct analytical computation of the spatial derivatives, which is more accurate than the computation with finite differences, is possible. A preliminary study on the use of higher order spatial derivatives for damage localisation on isotropic beams has been previously presented [1].
Two cases of damage are considered: (1) damage in the centre of the plate and (2) damage in the centre of the right upper quarter of the plate. The results of the present method are compared with results obtained with extensions of the well-known rotation and curvature methods [2,3] in two dimensions. Furthermore, besides computing the damage indicators at interior points of the plate using central finite differences, the present method also computes these indicators at the plate edges by differentiating the displacement fields using forward and backward finite differences.
The tests performed show that the results of all methods are mode dependent. Parametric studies carried out lead to the conclusion that, as the number of damaged measured degrees of freedom decreases, the success in damage localisation decreases. It was also found that the damage indicator based on the fourth order spatial derivative of the modal displacement field allows better damage localisations, in particular by considering the sum of the differences of these derivatives over a certain number of modes shapes.
-
- 1
- J.V. Araújo dos Santos, H.M.R. Lopes, N.M.M. Maia, "A damage localisation method based on higher order spatial derivatives of displacement and rotation fields", Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 305, 012008, 2011.
- 2
- M.A.-B. Abdo, M. Hori, "A numerical study of structural damage detection using changes in the rotation of mode shapes", Journal of Sound and Vibration, 251(2), 227-239, 2002.
- 3
- A.K. Pandey, M. Biswas, M.M. Samman, "Damage detection from changes in curvature mode shapes", Journal of Sound and Vibration, 145(2), 321-332, 1991.
|

